Low-Pressure Waterjet Solutions for Emergency Rescue
Water Cutting Technology: Low-Pressure Waterjet Solutions for Emergency Rescue
1. Introduction
In emergency rescue operations, time is critical and safety is non-negotiable. Conventional cutting and dismantling tools often involve sparks, heat, or mechanical impact, which can pose serious risks in hazardous environments.
Low-pressure waterjet technology, as an advanced cold-cutting solution, is increasingly recognized as a reliable and safe tool for emergency rescue applications. Using water as the cutting medium, it enables efficient material separation without sparks, heat-affected zones, or secondary ignition risks, while maintaining excellent environmental performance.
2. Conventional Cutting Methods vs. Water Cutting
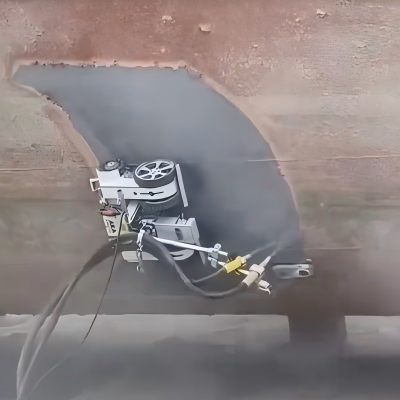
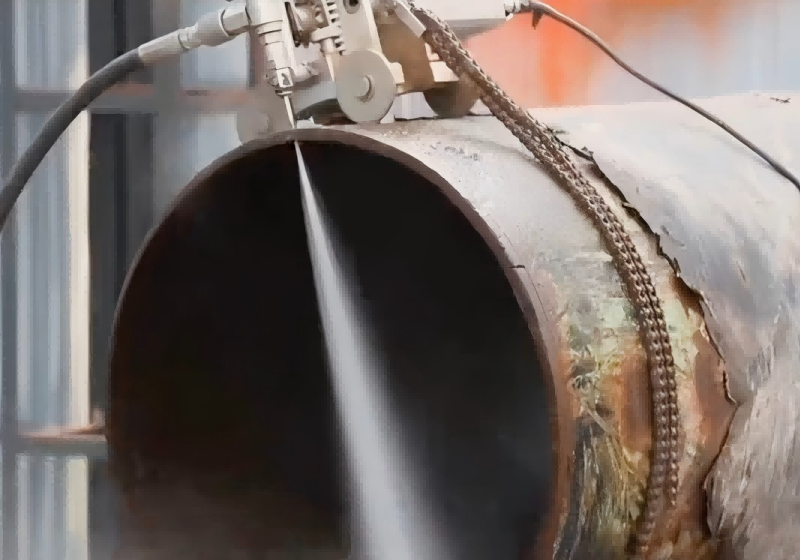
Low-pressure water cutting systems utilize pre-mixed abrasive waterjet technology, delivering true cold cutting performance. Unlike traditional mechanical or thermal cutting methods, water cutting eliminates hazards associated with high temperatures, static electricity, and sparks—key factors that can trigger explosions in rescue scenarios.
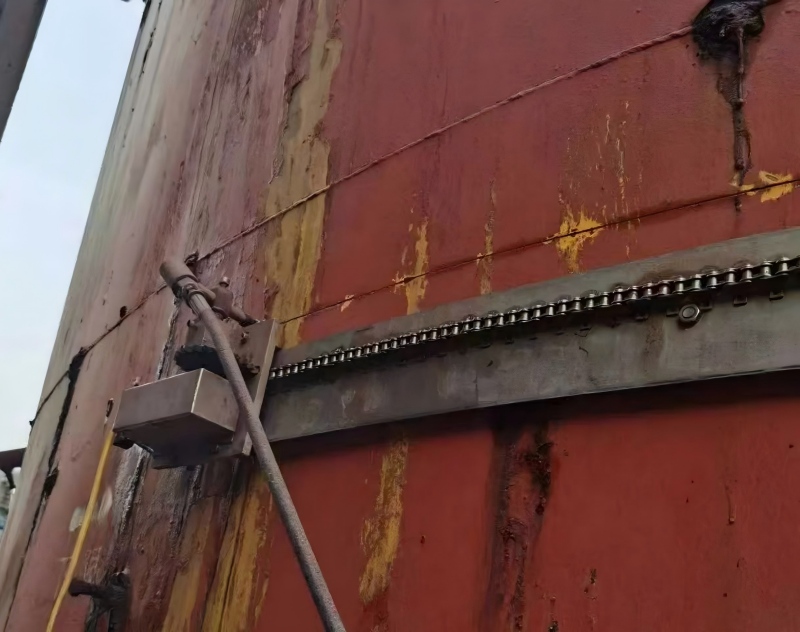
The technology preserves the original structural integrity of the material being cut, ensuring precise and controlled operations. Modern system designs support portable, integrated, and modular configurations. Through technological innovation, system weight has been reduced from over 2 tons to as little as 70 kg, allowing operation by just two personnel.
These systems can cut a wide range of solid materials with thicknesses from 1 to 100 mm, and can be vehicle-mounted, making them highly adaptable to complex and mobile emergency rescue environments.
3. Incident Overview: A Midnight Hazardous Materials Emergency
At 3:17 a.m. on January 8, 2026, a hazardous materials transportation accident occurred on the Shenhai Expressway. A tanker truck carrying 30 tons of methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) overturned while avoiding a vehicle that changed lanes abruptly. The tank suffered severe deformation, a rear valve failed, and a significant volume of flammable liquid began leaking.
The incident created an immediate high-risk situation involving fire, explosion, and environmental contamination, while the trapped driver required urgent rescue.
 |
 |
4. Hazard Analysis: Understanding MTBE Risks
MTBE is a colorless, highly flammable, volatile liquid with a strong ether-like odor, commonly used as a gasoline additive to improve octane ratings. Its key risk characteristics include:
-
High flammability with a low flash point
-
Strong water solubility, increasing environmental contamination risks
-
High volatility, allowing explosive vapor formation at ambient temperatures
-
Relatively low acute toxicity, but with irritating effects on eyes, skin, and respiratory systems
These properties make MTBE incidents extremely sensitive to ignition sources during rescue operations.
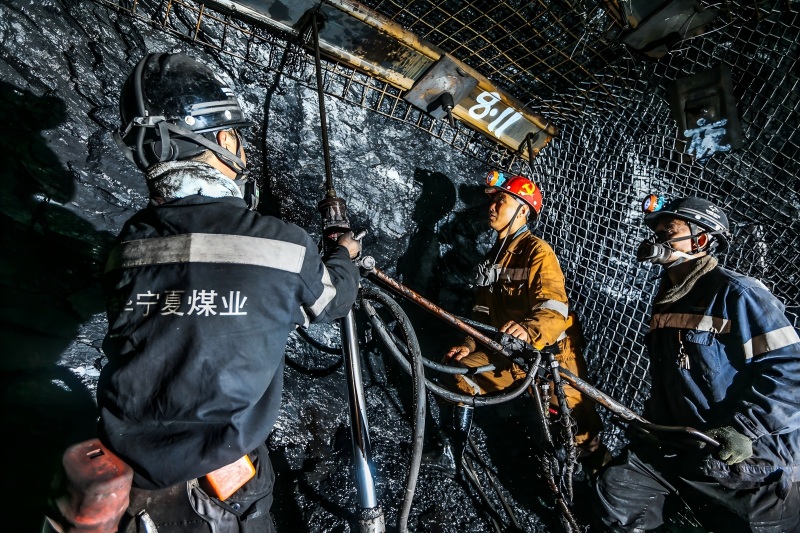
5. Rescue Strategy: Deploying Water Cutting Technology
After a comprehensive risk assessment and evaluation of available rescue methods, the incident command team selected low-pressure water cutting technology as the primary rescue solution. The decision was based on several critical advantages:
-
Intrinsic safety: No sparks, no static electricity, and no thermal impact
-
High precision and controllability, minimizing secondary damage to the tank
-
Environmentally friendly operation, using only water and abrasive media
-
Rapid execution, enabling fast access to trapped personnel
 |
 |
 |
6. Conclusion
This rescue operation highlights the unique advantages of low-pressure water cutting technology in emergency scenarios involving flammable, explosive, and hazardous materials. The successful outcome demonstrates its value as a safe, efficient, and reliable alternative to conventional cutting methods.
As waterjet technology continues to evolve, it is expected to play an increasingly important role in emergency rescue, hazardous materials response, and industrial safety operations—providing a higher level of protection for both rescue personnel and the public.